Milk-Specific IgE Reactivity Without Symptoms in Albumin-Sensitized Cat Allergic Patients
Karsonova AV, Riabova KA, Khaitov MR, Elisyutina OG, Ilina N, Fedenko ES, Fomina DS, Beltyukov E, Bondarenko NL, Evsegneeva IV, Glazkova PA, Semenov DY, van Hage M, Grönlund H, Karaulov AV, Valenta R, Curin M. Milk-Specific IgE Reactivity Without Symptoms in Albumin-Sensitized Cat Allergic Patients. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2021 Jul;13(4):668-670.
https://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2021.13.4.668
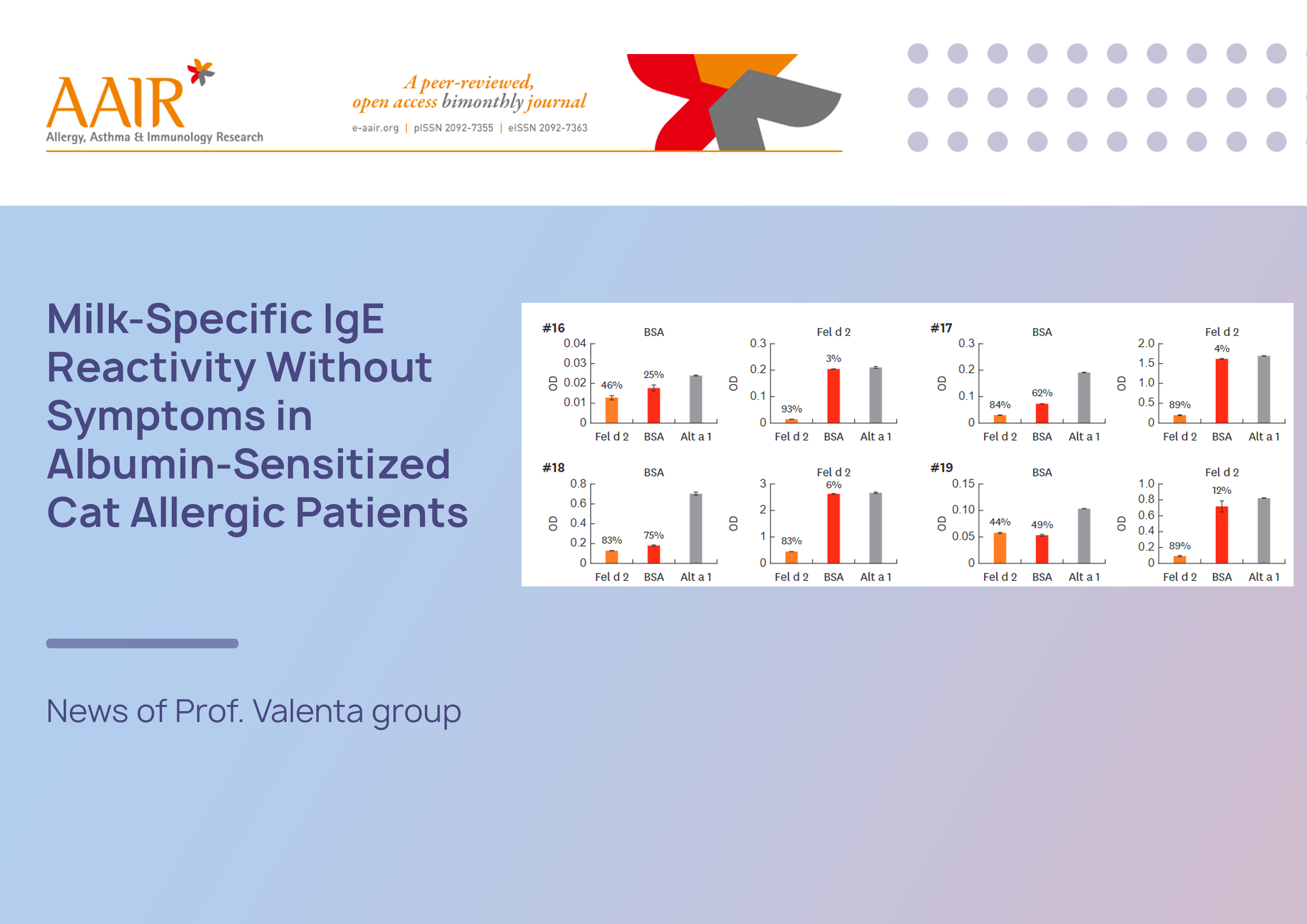
Serum albumin (Fel d 2) is a cross-reactive animal dander allergen, which can be found in animal-derived foods such as meat and milk.1 In a population study conducted in Moscow, Russia, we noted that milk albumin, Bos d 6, was more frequently recognized than the major milk allergens caseins, lactalbumin and lactoglobulin.2, 3, 4
We hypothesized that immunoglobulin E (IgE) sensitization to Bos d 6 could be attributed to original IgE-sensitization to cat dander via the respiratory tract and may be caused by IgE cross-reactivity between Fel d 2 and Bos d 6. Therefore, we studied a cohort of 85 patients with clinically documented allergy to cat. Using a panel of purified cat allergen molecules , we identified 15 patients who showed specific IgE reactivity (0.45–100 kUA/L) to cat albumin, Fel d 2 as tested by quantitative IgE ImmunoCAP. These patients suffered from various symptoms of allergy upon contact with a cat; however, each of them regularly consumed cow's milk and albumin-containing food, such as pork and beef, without experiencing any allergic symptoms. Further testing of these 15 Fel d 2-positive patients' sera showed that 7 out of the 15 patients showed IgE reactivity > 0.1 kUA/L to Bos d 6, 9 displayed IgE reactivity to cow's milk allergen extract and 5 were even positive to fx5, the mix of food allergen extracts including cow's milk in ImmunoCAP